What's a bearing
Today, bearings are one of the most commonly used machine componets because their rolling motion makes almost all movements easier while reducing friction.
Bearings have two key functions:
- Transfer motion, i.e. they support and guide components which turn relative to one another
- Transmit forces
Rolling bearings and sleeve bearings
In a sleeve or plain bearing, the axle and the bearing move in opposite directions on a sliding surface. By contrast, the two components of a rolling bearing that move towards one another – the inner and outer rings – are separated by rolling elements. This design generates significantly less friction than a sleeve bearing.
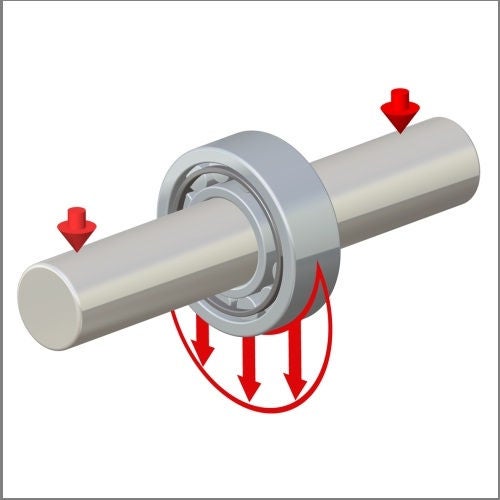
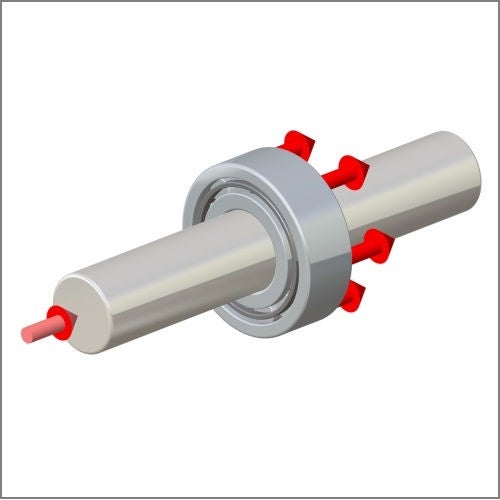
Radial bearings and axial bearings
Bearings can transmit loads in a radial direction or an axial direction (thrust) and in many cases there is a combination of both radial and axial loads to transmit.
Both designs are available as ball bearings or roller bearings. The choice of bearing design depends upon the application in question.
Components
Bearings typically consist of the following components:
- Two rings, inner and outer, with raceways
- Rolling elements - rollers or balls
- A cage which keeps the rolling elements spearted and helps guide motion
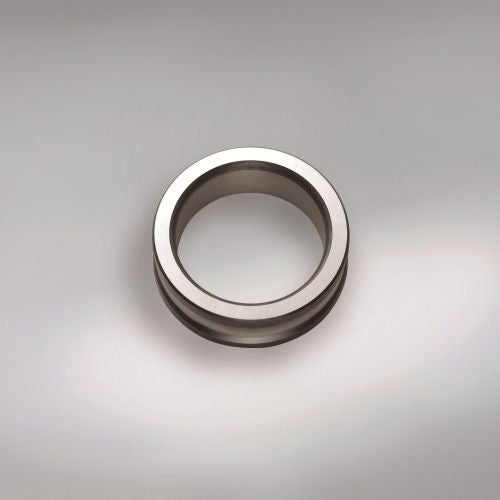
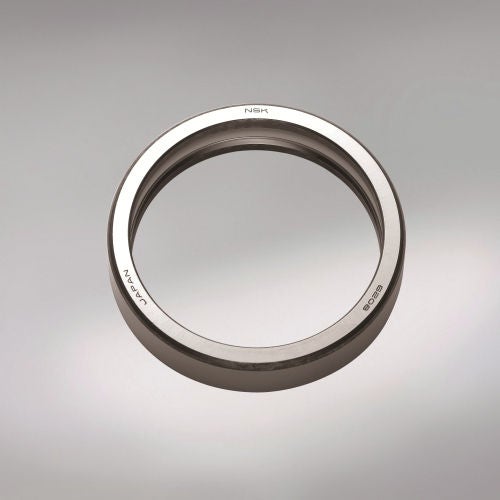
Inner Ring / Outer Ring
The inner and outer ring are typically made from a high-purity, chrome alloy steel. This material has the necessary hardness and purity important factors for high load ratings and a long service life.
The raceways are hardened, ground and honed.
Special materials such as ceramic and plastics are also prduced. Although plastics cannot withstand extremely high temperatures, they are considerably lighter than steel which makes them invaluable in sectors such the automotive industry, where every ounce matters.
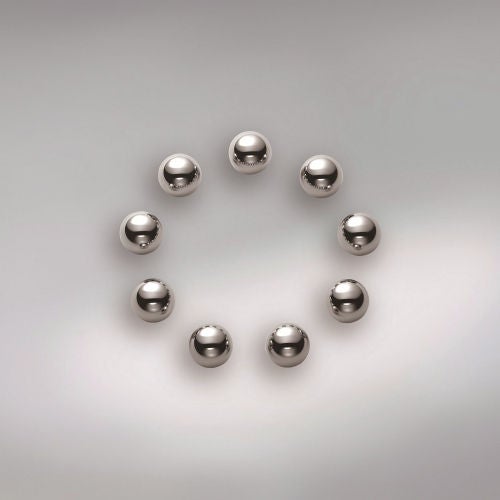
Rolling elements
Rolling elements are either balls, rollers, cones, spheres or needles. They are usually made from a special high-purity, chrome alloy steel. Special materials such as ceramic and plastics are also used.
The rolling elements roll on the specially formed raceways of the rings or discs and are kept apart and guided by the cage.
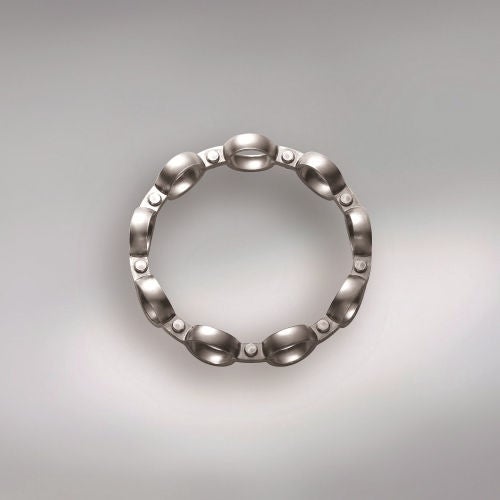
Cage
The cage is responsible for keeping the rolling elements apart and guiding them. The materials used include steel, brass and plastic. Solid metal cages can be produced using machining techniques, while pressed cages are made from sheet metal. Similarly, plastic cages can be machined from solid plastic or injection moulded.




Share