NSK Ltd.
Corporate Communications Department
NSK Develops MT-Frix™ Low-Friction Ball Screws for Machine Tools
Significant reduction in dynamic friction torque and heat generation of ball screws for more sustainable machine tool accuracy and better energy savings
- Applying NSK’s analytical technology made it possible to clarify the contact condition between the ball and groove to develop optimal internal specifications.
- Using those optimal internal specifications, NSK was able to reduce dynamic friction torque while maintaining nut rigidity using the same dimensions enabling significant heat reduction.
- Sustains high positioning accuracy and reduces CO2 emissions caused by dynamic friction torque by up to 50% compared to conventional products.
NSK Ltd. (NSK; Headquarters: Tokyo, Japan; President and CEO: Akitoshi Ichii) has developed MT-Frix*1, a low-friction ball screw. By clarifying the contact condition between the ball and groove inside the ball screw using NSK's analytical technology and optimizing the internal specifications, dynamic friction torque has been reduced while maintaining nut rigidity*2 and while keeping the same dimensions. As a result, significant heat reduction has been achieved, sustaining the high positioning accuracy of machine tools and reducing CO2 emissions caused by dynamic friction torque*3 by up to 50% compared to conventional products.
NSK will exhibit this product the 32nd Japan International Machine Tool Fair (JIMTOF 2024), which will be held from November 5 to November 10, 2024. Orders from customers are scheduled to start in April 2025. NSK sales goal for this series is 500 million yen by 2027.
*1 MT-Frix™: The origin of the name is MT (short for “machine tool”) + Frix (short for “friction”). The intent of the product name is "a ball screw with friction characteristics that are optimal for machine tool applications ".
*2. Rigidity: The resistance to deformation due to external load"
*3. Dynamic friction torque: The torque caused by friction generated when rotating a ball screw
The newly developed product
1. Development Background
Ball screws are mounted on the linear drive units of machine tools and are responsible for positioning the machining tools and workpieces. In recent years, there has been a growing need for higher positioning accuracy and energy saving in ball screws as well, due to the advancement of machining and decarbonization.
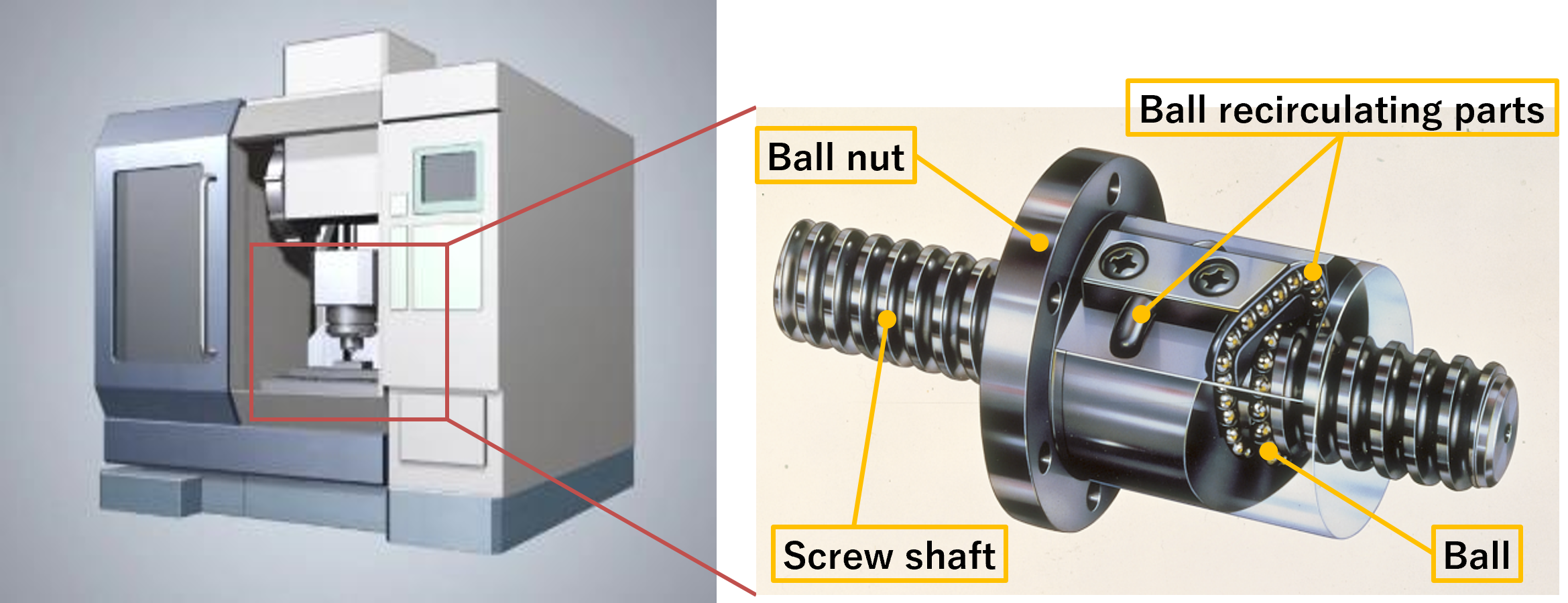
Ball screw installation position in a machine tool
When a ball screw is driven, it generates heat due to dynamic friction torque, and the screw shaft undergoes thermal expansion, which in turn reduces the positioning accuracy. In order to prevent accuracy loss due to heat generation, forced cooling (cooling the generated heat with an auxiliary device, etc.) may be used, but extra energy is consumed when a cooling device is employed. Therefore, in order to achieve both high precision and energy savings, it is necessary to reduce the dynamic friction torque itself.
However, with conventional technology, when the dynamic friction torque is reduced, the rigidity also declines, making the nut more likely to experience displacement, which in turn can result in the problem of reduced machining accuracy. Therefore, reducing dynamic friction torque while maintaining rigidity is needed.
2. Technology of the Newly Developed Product
NSK's analytical technology was used to clarify the contact condition between the ball and groove, which made it possible to develop optimal internal specifications.
⇒ Dynamic friction torque was reduced while maintaining nut rigidity and while keeping the same dimensions of the ball screw.
3 . Features of the Developed Product
Reduced dynamic friction torque and heat generation while maintaining the dimensions.
1) Reduction of dynamic friction torque: Nut rigidity is equivalent to the conventional product, and dynamic friction torque has been reduced by up to 50% compared to the conventional product.
2) Reduction of heat generation: Due to the reduction in dynamic friction torque, heat generation (temperature rise value) during ball screw driving has been reduced by up to 40% compared to the conventional product.
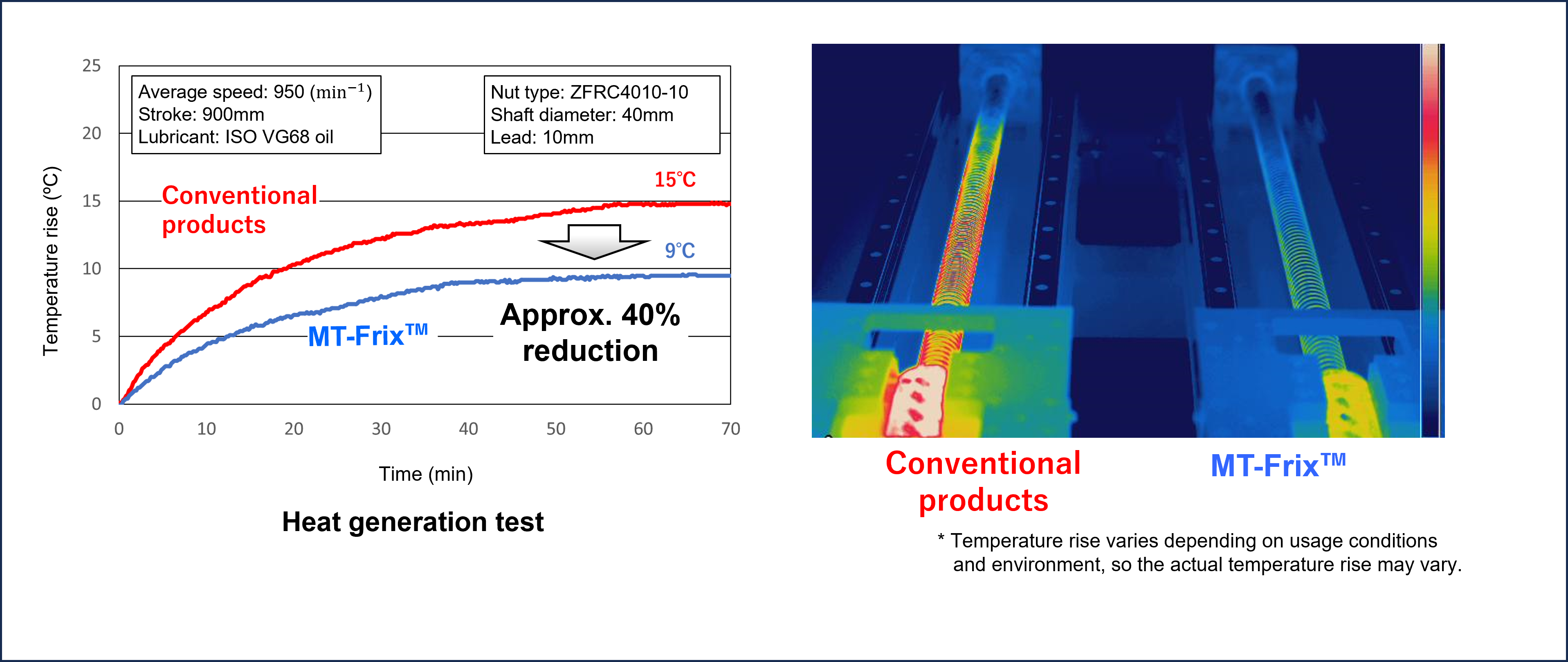
Results of heat generation test (left) and temperature distribution during the test (right)
4 . Benefits for Machine Tools
1) Sustained high positioning accuracy: By reducing heat generation, the amount of axial elongation is reduced by up to 40% compared to conventional products, reducing the deterioration of positioning accuracy.
2) Energy savings: CO2 emissions caused by dynamic friction torque have been reduced by up to 50% compared to conventional products.
Example of estimated CO2 reduction effect due to dynamic friction torque (based on NSK internal findings)
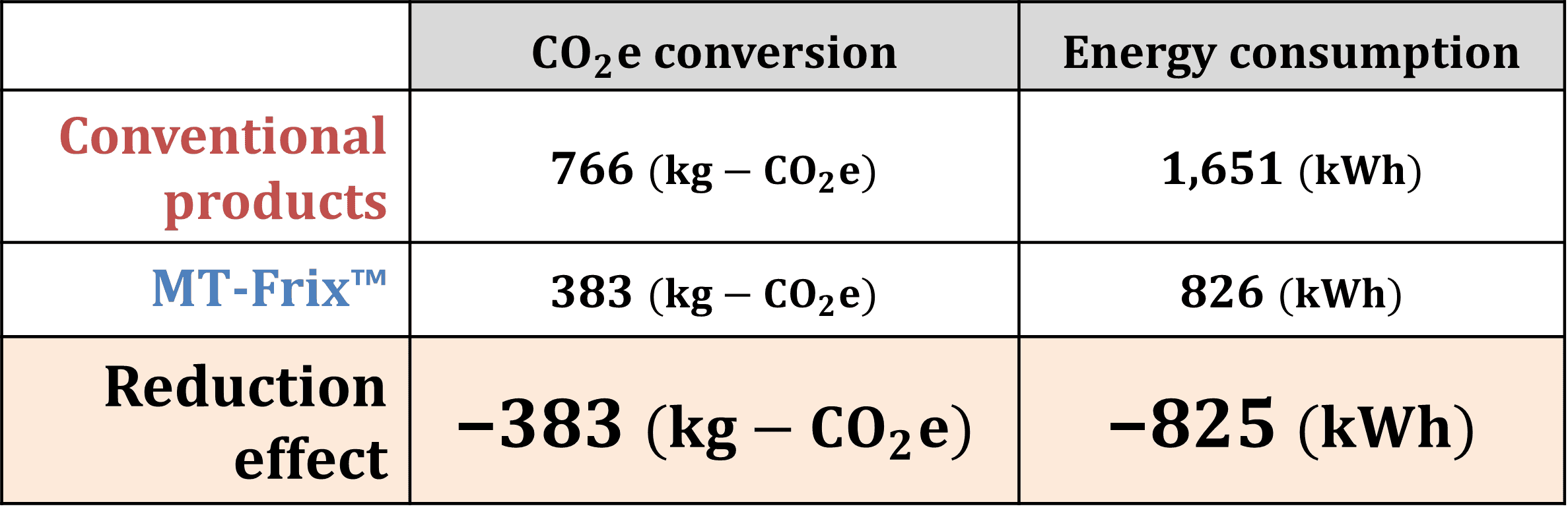
Calculation conditions:
Ball screw specifications: Shaft diameter 40 mm, lead 10 mm, total length 1400 mm
Period of use: 5 years
Average speed: 400 min-1
CO2 Emission Factor: 0.4641 kg− CO2/kWh (applied during use)
About NSK
NSK produced the first bearings in Japan in 1916 and over the past 100 years, it has supported the development of industries worldwide by creating various innovative products and technologies in bearings, automotive parts, and precision machinery. Since the early 1960s, the company has expanded overseas and now has operations in about 30 countries. It ranks third in the world in the field of bearings and leads the world in ball screws, electric power steering, and other products.
