Risk Management
NSK’s Approach
At the NSK Group, the executive management team oversees the implementation of a risk management system guided by the Group’s basic internal control policy. Risks faced by the NSK Group are identified, categorized and prioritized by the risk management department, before being assigned to responsible departments. This system is designed to avoid and minimize risks for the entire Group and to coordinate response measures when risks actually materialize.
System
Risk Management Systems
NSK conducts risk management based on clearly stipulated fundamental principles aimed at effectively enabling the Group global management and internal control functions.
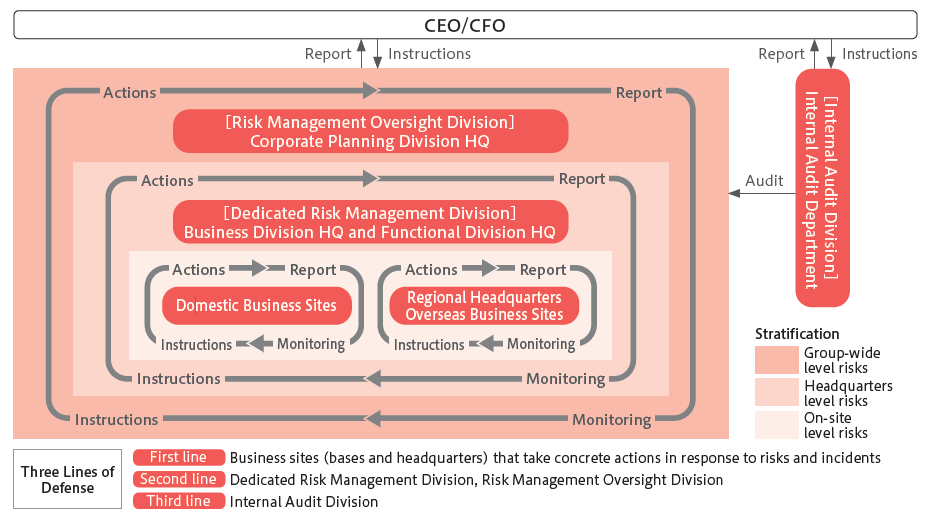
To increase the effectiveness of risk management, NSK established a new Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework setting out more clearly the “Three Lines of Defense” approach.
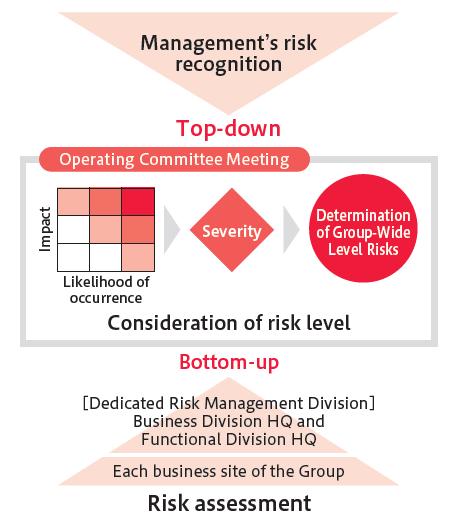
Key pillars for operation of this new framework are the introduction of risk stratification and enhancement of potential risk management. In terms of stratification, based on management’s risk recognition and instructions, risks identified through Group-wide risk assessments were divided into three categories: Group-wide level risk, headquarters-level risk, and on-site level risk, and responsibility for addressing each risk was clarified. The Operating Committee determines Group-wide material risks based on a consideration of their severity in addition to an evaluation of the likelihood of occurrence and impact and provides a report to the Board of Directors. In addition, for each risk identified, we determine countermeasures from the viewpoints of avoiding, mitigating, transferring, or accepting risk and seek more effective means of preventing risks from materializing through a cycle that entails the taking and reporting of such actions, as well as monitoring and giving instructions. At the same time, we adopt a system where, in the event of an incident, the dedicated risk management division (Business Division Headquarters or Functional Division Headquarters) in charge of managing the relevant risk seeks to mitigate the impact by working with the affected business site to take prompt and appropriate steps and assumes responsibility until the incident is over. The Risk Management Oversight Division (Corporate Planning Division Headquarters) shares the latest risk management situation with management and provides opportunities to encourage an understanding of such.
In addition, the internal audit division (Internal Audit Department), which is independent of the executive divisions, checks the ERM system framework and reports its findings to the Audit Committee.
Determination of Group-Wide Level Risks
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) System
Representative Risks and Countermeasures
| Risk Item | Details of Representative Risks | Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Risks associated with technological innovation |
|
|
| (2) Risks associated with safety, prevention of fire, and natural disasters |
|
|
| (3) Risks associated with quality |
|
|
| (4) Risks associated with the environment |
|
|
| (5) Risks associated with compliance |
|
|
| (6) Risks associated with human resources and labor |
|
|
| (7) Risks associated with procurement |
|
|
| (8) Risks associated with DX and information security |
|
|
| (9) Risks associated with mid- to long-term improvement in corporate value |
|
|
